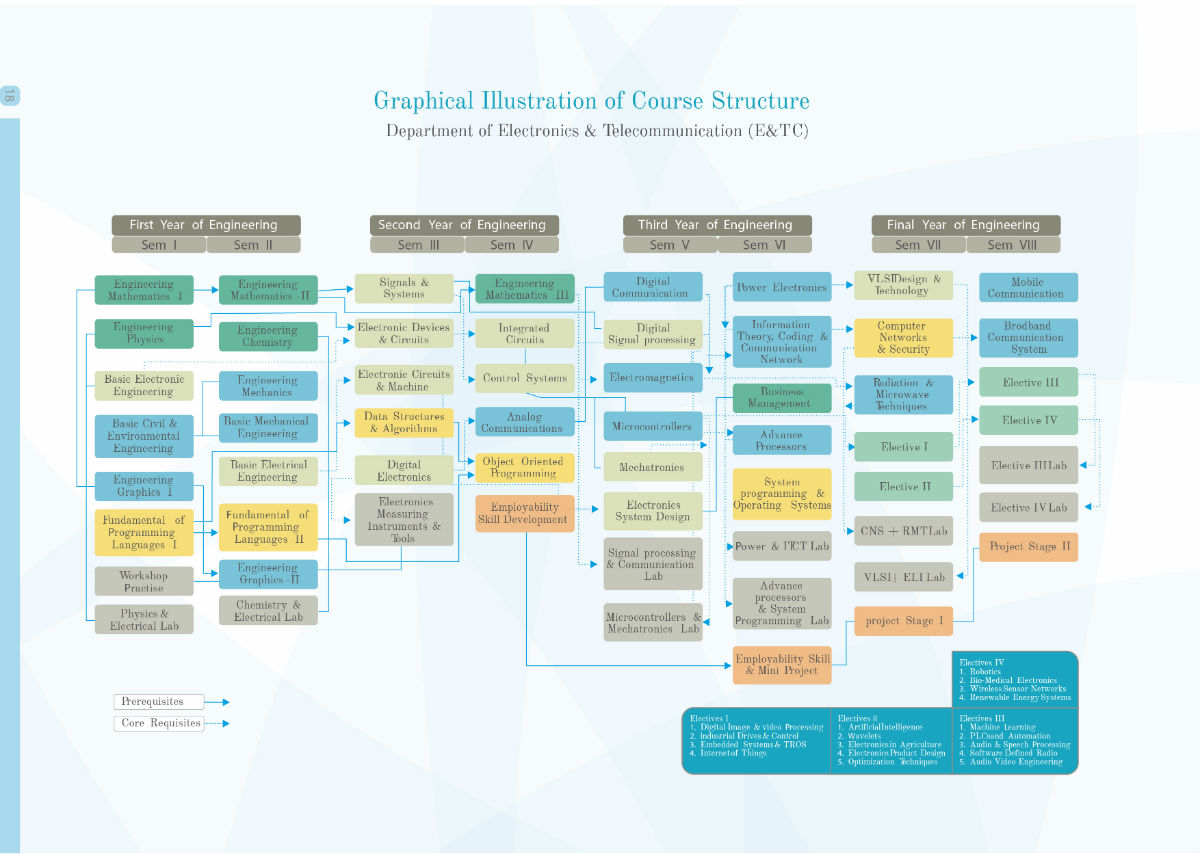
About the Program
Electronics and Telecommunication course was launched in the academic year 2011-12 with a total intake of 60. The Department has well-established state-of-the-art computer laboratories and classrooms that are equipped with ICT tools and computing facilities. Other than academics, the department provides its students with opportunities to participate in co-curricular and extra-curricular activities to showcase their talents and skills. The program aims towards an all-round development of students to mould them into becoming competent for the industry, academia and / or research.